A Tale of Two Forwarded Headers


This is the story of how I handled troubleshooting the redirect URL for OAuth2 in Appsmith, which contained the host as localhost instead of the actual domain name when hosted on Google Cloud Run. We’ll talk about how the Forwarded and X-Forwarded-* headers were propagating through multiple reverse proxies and how they can be confused.
The Problem
Appsmith is an internal tool builder that has a React-based frontend and a Java+Spring based backend server. This backend uses the spring-security module's support for OAuth2 authentication, which enables logging in to Appsmith with Google.
Google Cloud Run is
[...] a managed compute platform that lets you run containers directly on top of Google's scalable infrastructure.
In other words, Google Cloud Run is a serverless abstraction to run Docker containers.
When running Appsmith on Google Cloud Run and enabling Login with Google, the redirect URL used as part of the OAuth2 flow includes the host as localhost instead of the actual domain name. This causes the OAuth2 flow to fail due to a mismatch in the redirect URL. Appsmith is shipped as a single Docker image.
Primary Behaviour
With Google OAuth configured, let’s start an Appsmith container and see what redirect URL gets generated in a controlled environment.
docker run --name appsmith -p 8001:80 -v stacks:/appsmith-stacks -d \
-e APPSMITH_OAUTH2_GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID=dummy \
-e APPSMITH_OAUTH2_GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET=dummy \
appsmith/appsmith-ce:v1.9.29
We configure Google OAuth with dummy values here, since we only care about the generated redirect URL. We are not concerned about the complete OAuth flow.
Let's wait a little while for that to start and show up working on http://localhost:8001. Then let's initiate the OAuth2 flow and see the redirect URL.
curl -sSi http://localhost:8001/oauth2/authorization/google
This will print all the response headers. Let's just pick the redirect_uri query parameter in the Location header (which contains the Google authorization endpoint as part of the OAuth2 flow).
curl -sSi http://localhost:8001/oauth2/authorization/google | grep -Eo 'redirect_uri=[^&]+'
We get the result as this:
redirect_uri=http://localhost/login/oauth2/code/google
Which is not entirely accurate because it's missing the :8001 part, but that's a problem for another day. For now, let's just focus on the localhost part. This is the correct host here. But if we make this request with a different host:
curl -sSi http://localhost:8001/oauth2/authorization/google \
-H 'Host: one.com' | grep -Eo 'redirect_uri=[^&]+'
Here, in the redirect_uri query parameter, we expect to see http://one.com/login/oauth2/code/google, which we indeed do.
redirect_uri=http://one.com/login/oauth2/code/google
Similarly, if we try with X-Forwarded-Host header or the more standard Forwarded header, we always see the correct host in the redirect_uri query parameter.
curl -sSi http://localhost:8001/oauth2/authorization/google \
-H 'X-Forwarded-Host: two.com' | grep -Eo 'redirect_uri=[^&]+'
redirect_uri=http://two.com/login/oauth2/code/google
curl -sSi http://localhost:8001/oauth2/authorization/google \
-H 'Forwarded: host=three.com' | grep -Eo 'redirect_uri=[^&]+'
redirect_uri=http://three.com/login/oauth2/code/google
The Appsmith backend server seems to be handling the host detection quite well, but when it's run on Google Cloud Run, the host is always localhost.
curl -sSi https://appsmith-abcdefghij-uc.a.run.app/oauth2/authorization/google \
-H 'Host: four.com' | grep -Eo 'redirect_uri=[^&]+'
redirect_uri=http://localhost/login/oauth2/code/google
Cloud Run, the Reverse Proxy
We've established that if the host is shared correctly with Appsmith, it produces the correct redirect_uri. So something about the way Google Cloud Run is forwarding the host is not working as expected. We want to find out just what Cloud Run is sending across.
To get this information, let's run an instance of httpbun on Cloud Run, which can respond with all the headers it receives.
Here's a sample configuration of how we can run this httpbun on Cloud Run.
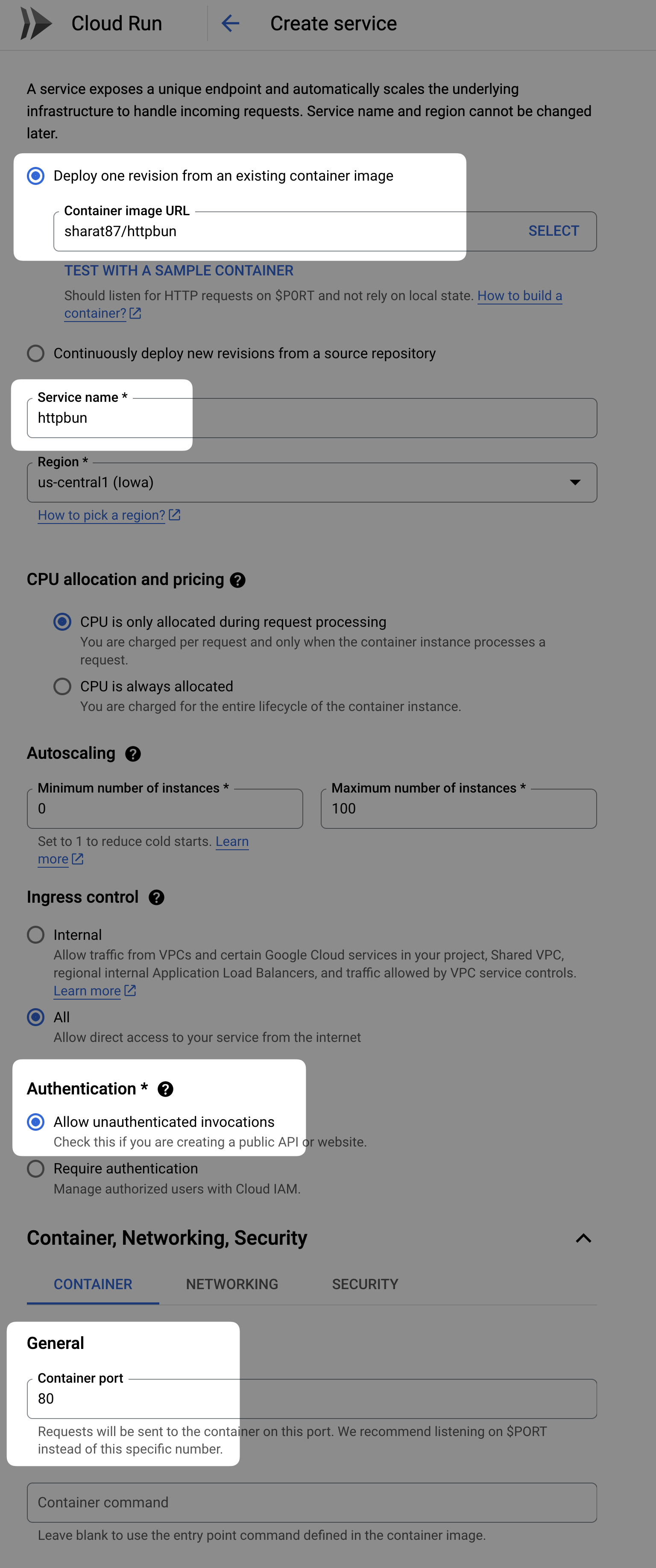
Once this is deployed, we get a URL like https://httpbun-abcdefghij-uc.a.run.app. Let's make a request to this and see what headers it reports as part of the request.
curl -sSi https://httpbun-abcdefghij-uc.a.run.app/headers
{
"Accept": "*/*",
"Forwarded": "for=\"1.2.3.4\";proto=https",
"Host": "httpbun-abcdefghij-uc.a.run.app",
"Traceparent": "00-abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzabcdef-ghijklmnopqrstuv-01",
"User-Agent": "curl/7.88.1",
"X-Cloud-Trace-Context": "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzabcdef/ghijklmnopqrstuvwxy;o=1",
"X-Forwarded-For": "1.2.3.4",
"X-Forwarded-Proto": "https"
}
Fantastic! We see that Cloud Run sends the actual host in the Host header, instead of X-Forwarded-Host, despite sending in X-Forwarded-For and X-Forwarded-Proto. This is only slightly odd, but not groundbreaking. As we've seen earlier, Appsmith handles this just fine.
But in addition to that, notice that we have a Forwarded header too. This contains the same information as X-Fowarded-For and X-Forwarded-Proto, and doesn't contain a host field.
Detour: The
Forwardedheader is a more standard header that holds the same (and some more) information as theX-Forwarded-*suite of headers, which is are a little less standardly defined. What's peculiar here is that Cloud Run appears to be sending bothForwardedandX-Forwarded-*headers.
We didn’t test this case with our local Appsmith. That is, we didn’t send the actual host in the Host header, but also include a Forwarded header with information about the origin protocol (and IP Address). Let's do that now.
curl -sSi http://localhost:8001/oauth2/authorization/google \
-H 'Host: abc.com' -H 'Forwarded: for"1.2.3.4";proto=https' | grep -Eo 'redirect_uri=[^&]+'
redirect_uri=https://localhost/login/oauth2/code/google
Boom! There it is. Although we're sending the host in Host header, Appsmith responds with localhost in the host part of the redirect_uri. This is the same behavior we see on Cloud Run.
The Reverse Proxy Inside Appsmith Container
Inside the Appsmith container, we have an NGINX process that handles all incoming requests. If the request points to a static file, it is served immediately. If it points to a backend API call, NGINX will proxy the request over to the Appsmith backend server. This NGINX configuration file is generated by this script and you can peek into the actual configuration used by running docker exec appsmith cat /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default. For the URL we've been curl-ing so far, the route that matches is this:
location /oauth2 {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080;
}
Since this location block doesn't have any proxy_set_header directives, the ones in the parent context will apply. We can see these as:
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $origin_scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $origin_host;
The $origin_scheme and $origin_host are defined at the top of the configuration file, as shown below:
map $http_x_forwarded_proto $origin_scheme {
default $http_x_forwarded_proto;
'' $scheme;
}
map $http_x_forwarded_host $origin_host {
default $http_x_forwarded_host;
'' $host;
}
What this is essentially doing is setting up so that if the incoming request has an X-Forwarded-Proto header, the $origin_scheme is set to that header's value. If that header is not present in the request, $origin_scheme is set to $scheme. This is an NGINX variable set to the current request's protocol. Similarly, $origin_host either takes the value of X-Forwarded-Host header if present or the current request's host (which is usually the Host header of the request).
This means that once the request goes from this NGINX to Appsmith backend server, Host becomes localhost:8080, X-Forwarded-Host is set to appsmith-abcdefghij-uc.a.run.app, and the others X-Forwarded-Proto, X-Forwarded-For, and even the Forwarded header, are passed along as is.
This is the problem.
Since the Forwarded header is the more modern standard, its value usually takes precedence. The fact that the request has a Forwarded header, unfortunately, means that all the other X-Forwarded-* headers will be ignored by the Appsmith server.
This means the X-Forwarded-Host header is completely ignored and the server instead looks for a host= field in the Forwarded header, which is missing, so it thinks the host it receives in the Host header, localhost:8080, is the actual host, and uses that to construct the redirect_uri.
We can simulate this theory by sending a request to the Appsmith backend server directly instead of going through the NGINX proxy. We can do this by using the docker exec command. Here’s an example:
docker exec appsmith curl -sSi localhost:8080/oauth2/authorization/google \
-H 'Forwarded: for="1.2.3.4";proto=https' \
-H 'X-Forwarded-Host: abc.com' \
| grep -Eo 'redirect_uri=[^&]+'
redirect_uri=https://localhost/login/oauth2/code/google
This produces localhost in the redirect_uri, just like we saw earlier, instead of abc.com. If we remove the Forwarded header, or add host= field in it, it works just fine.
docker exec appsmith curl -sSi localhost:8080/oauth2/authorization/google \
-H 'X-Forwarded-Host: abc.com' \
| grep -Eo 'redirect_uri=[^&]+'
redirect_uri=https://abc.com/login/oauth2/code/google
docker exec appsmith curl -sSi localhost:8080/oauth2/authorization/google \
-H 'Forwarded: for="1.2.3.4";proto=https, host=abc.com' \
-H 'X-Forwarded-Host: abc.com' \
| grep -Eo 'redirect_uri=[^&]+'
redirect_uri=https://abc.com/login/oauth2/code/google
The Solution
In the NGINX, we add/set the X-Forwarded-Host header, at all times, which is the right thing to do. But if the incoming request has a Forwarded header, it takes precedence and the X-Forwarded-Host header is ignored. This is the problem.
So we get NGINX to also add the host= field, if a Forwarded header exists. We do this in this PR.
Essentially, define a $final_forwarded as shown below:
map $http_forwarded $final_forwarded {
default '$http_forwarded, host=$host;proto=$scheme';
'' '';
}
In the http block, we set the Forwarded header as follows:
proxy_set_header Forwarded $final_forwarded;
This way, if there's no incoming Forwarded header, we don't send it to the backend server either. But if it exists, we add the host= field (and a proto= field for good measure) to it, and send it to the backend server.
Conclusion
The confusion between Forwarded and X-Forwarded-* suite of headers, and which takes precedence when both are set, turned out to be the underlying problem. The NGINX we use inside Appsmith, was only ever tuned to work with X-Forwarded-* suite of headers. Additionally, since Google Cloud Run is so opaque, in the sense that we can't even get shell access into the running container, using tools like Httpbun can be very helpful in figuring out what details the request actually contains.